Did you know that up to 40% of men over 45 may have low testosterone, but most remain undiagnosed? Low testosterone, or male hypogonadism , is more common than many realize and can silently wreak havoc on your health, mood, and vitality. Whether you're feeling unusually tired, noticing a dip in your sex drive , or simply wondering if something is off, understanding the signs and symptoms of low testosterone could be the key to regaining your well-being. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll uncover the latest facts, learn how to spot low testosterone, and discover both medical and natural solutions to support your testosterone levels—and your quality of life.

Revealing the Prevalence of Low Testosterone: Why Addressing Testosterone Levels Is Crucial
Low testosterone or "low-T" isn't a rare problem; in fact, millions of men are struggling with it without even knowing. Studies estimate that only about 5–10% of men with symptoms of low testosterone ever discuss them with their healthcare providers. This silent health issue can affect anyone—men of all ages, backgrounds, and lifestyles. Yet, it is rarely talked about openly, resulting in unnecessary suffering. Recognizing and addressing low testosterone early can drastically improve quality of life and prevent serious health complications later on.
Addressing testosterone levels is crucial as this hormone doesn’t just influence sex drive and muscle mass—it’s central to bone density , mood , energy, and overall health. Ignoring symptoms of low testosterone may lead to persistent fatigue, decreased motivation, and even increased risk of conditions like osteoporosis and heart disease. Taking charge by understanding the importance of healthy testosterone levels is the first step toward feeling your best at every age.
A Startling Truth: Millions Live With Undiagnosed Low Testosterone
One of the most surprising realities is how many cases of low testosterone go unnoticed and untreated. Many men attribute their fatigue, low mood, and other symptoms to aging or stress, never realizing they may be living with low testosterone levels . Without proper assessment, they continue to suffer in silence. However, awareness is growing, and more individuals are now seeking assessment for their testosterone level when persistent symptoms appear. If you suspect that something feels off, you aren’t alone—millions may share your experience and stand to benefit from increased awareness and accessible testing.
The importance of recognizing this problem cannot be overstated. Left unchecked, low testosterone can have compounding effects on everything from day-to-day motivation to long-term physical health. Understanding that you’re not alone, and that help is available, is a powerful motivator to take action.
Understanding the Impact of Low Testosterone on Health and Daily Life
Low testosterone doesn’t just affect sexual health. Men with low T often report diminished energy, difficulty concentrating, hot flashes , and mood swings. Lower muscle mass and persistent fatigue become common complaints that disrupt work and family life. For some, low testosterone can even undermine self-confidence and mental well-being, making it tough to maintain the motivation to exercise or eat healthily.
The effects stretch far beyond the bedroom. Over time, untreated low testosterone may increase risks for developing osteoporosis (due to decreased bone density ), metabolic syndrome, and even cardiovascular problems. Mental health can also suffer; men often report increased rates of depression and irritability. Recognizing the significant reach of this hormone is the foundation for seeking real solutions and regaining control of your vitality.
It's also important to note that low testosterone is just one aspect of a broader hormonal landscape. If you're curious about other visible signs that may indicate a hormone imbalance, you might find it helpful to review these seven visible signs of hormone imbalance that can offer additional clues about your overall health.
What Low Testosterone Means: Defining Testosterone Level and Clinical Low Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone in men, crucial for everything from sperm production to muscle mass and sex drive. Low testosterone (or testosterone deficiency) is defined when blood tests reveal levels below a certain threshold—typically under 300 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL)—combined with persistent signs and symptoms such as fatigue and low libido. Clinical diagnosis is more than just numbers on a lab report; it’s about connecting symptoms with measured testosterone levels to determine if treatment or further investigation is necessary.
The diagnosis of low testosterone often involves repeating the measurement since testosterone levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day. Most often, a morning blood test is advised for the most accurate reading. Understanding both your numbers and your symptoms is essential for a diagnosis of male hypogonadism or low testosterone. If you’re unsure about your readings or what they mean, discussing your results with a healthcare provider who specializes in hormonal health can provide much-needed clarity.
| Age Group | Normal Range (ng/dL) | Low Testosterone (ng/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| 18-39 years | 300-1,000 | <300 |
| 40-59 years | 250-900 | <250 |
| 60+ years | 200-800 | <200 |
Recognizing Symptoms of Low Testosterone: Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of low testosterone can be challenging since many are subtle or overlap with other conditions. The most common signs and symptoms include decreased energy (fatigue) , loss of sex drive , mood changes, and issues such as difficulty concentrating. For many, symptoms like hot flashes, decreased muscle mass , and erectile dysfunction are especially concerning. What appears as normal aging may, in fact, point to a correctable hormonal imbalance.
These symptoms can appear singly or in combination and may develop slowly, making them easy to overlook. Sometimes, changes in motivation or persistent feelings of sadness signal underlying testosterone deficiency rather than an isolated mood disorder. Recognizing these patterns—and associating them with potential hormonal changes—can prompt early conversations with your healthcare team, leading to faster diagnosis and relief.
- Fatigue
- Low sex drive
- Mood changes
- Difficulty concentrating
- Hot flashes
- Decreased muscle mass
- Erectile dysfunction

Unique Symptoms of Low Testosterone in Different Age Groups
While low testosterone levels can affect males at any age, the signs and symptoms may look different as you move through life's stages. In young boys, low testosterone may delay puberty, impair growth, and limit the development of muscle, bone, and facial hair. For adult men, a sudden loss in sex drive , declining muscle mass , and changes in libido are typical red flags. Seniors may experience persistent fatigue, loss of interest in activities, and low blood counts, with symptoms easily misattributed to aging.
The overlap between normal aging and low testosterone means that some symptoms—like decreased motivation or memory issues—may be dismissed. However, it's important to distinguish what's expected from growing older and what's a sign of a treatable hormonal problem. If you’re unsure, consider a blood test to clarify whether testosterone deficiency might be a factor in your symptoms.
The Overlap: Symptoms of Low Testosterone vs. Other Health Issues
Many symptoms of low testosterone also appear in other health conditions, adding to the confusion. Fatigue, low mood, sleep changes, and erectile dysfunction are common in diabetes, depression, or thyroid disorders as well. Even hot flashes —often thought to be exclusive to women—can be a manifestation of hormonal imbalance in men. Because of this overlap, it’s critical for any man with persistent symptoms to seek comprehensive medical evaluation.
Treating only the symptom, without looking for an underlying hormonal cause, may short-change your recovery. That’s why a healthcare provider will often recommend tests for testosterone level alongside other possible causes before deciding on the best course of action.
Assessing Testosterone Levels: Diagnostic Tests, Measurements, and What Results Mean
The only way to know if you have low testosterone is to check your testosterone level through a blood test. Doctors typically measure total testosterone using a morning sample, when values are highest. Sometimes additional measurements, such as free testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin ( sex hormone levels), are required for an accurate diagnosis. Blood tests not only confirm low levels but can also help determine if the problem is due to primary hypogonadism (testes issues) or secondary hypogonadism (brain or pituitary gland issues).
After your blood tests, your doctor will interpret the numbers in the context of your signs and symptoms . If your levels of testosterone are repeatedly low—and you're having symptoms of low testosterone—diagnosis and treatment may be recommended. Re-testing and monitoring are often needed because testosterone levels fluctuate throughout the day and with lifestyle changes, illness, or medication.

How Doctors Measure Testosterone Level and Interpret Results
To provide an accurate assessment, most clinicians recommend a blood test drawn early in the morning—testosterone peaks between 7 and 10 a.m. If the result is below 300 ng/dL on more than one occasion and you’re experiencing classic symptoms of low testosterone , the diagnosis is confirmed. Additional hormone tests may be necessary to distinguish between primary hypogonadism and secondary hypogonadism —which can impact not only treatment but also prognosis.
"A simple morning blood test can reveal if your testosterone levels are abnormally low. Regular evaluation is key for long-term health." — Endocrinologist
Diagnostic bloodwork may also include a comprehensive hormone panel covering FSH, LH, prolactin, the pituitary gland hormones, and markers for other systemic diseases. This thorough approach ensures an accurate diagnosis and helps eliminate other potential contributors to your symptoms.
When to Check for Low Testosterone Levels: Recognizing Triggers and Thresholds
If you’re experiencing unexplained fatigue, low sex drive, erectile dysfunction , muscle loss, or mood changes, you should consider a check of your testosterone level . Other triggers include infertility, osteoporosis, or existing conditions like pituitary disease. Persistent symptoms—even if mild—warrant discussion with your healthcare provider. Early testing is important, as prompt diagnosis of low testosterone can provide a clear path to solution and better health.
Don’t wait for symptoms to become severe; a proactive approach with timely blood tests enables you to catch problems early and start appropriate therapy before more severe issues arise.
Understanding the Causes: What Leads to Low Testosterone and Male Hypogonadism
A variety of factors can contribute to low testosterone levels . In many men, levels naturally decline with age—particularly after 30. However, other causes include disease or injury affecting the testes, problems with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, medication side effects, or chronic health conditions like diabetes. Understanding what’s causing your low blood testosterone is crucial to choosing the right treatment. Certain genetic conditions like Klinefelter syndrome or a history of trauma to the groin can also impair normal testosterone production.
- Aging
- Pituitary gland dysfunction
- Primary hypogonadism
- Secondary hypogonadism
- Chronic illness
- Medications
Some medications, especially steroids and opioids, can have a significant impact on testosterone production . Chronic stress and poor lifestyle factors—such as obesity and heavy alcohol intake—also play a role in lowering levels. It’s essential to recognize and address both reversible and irreversible causes of low testosterone for optimal management.
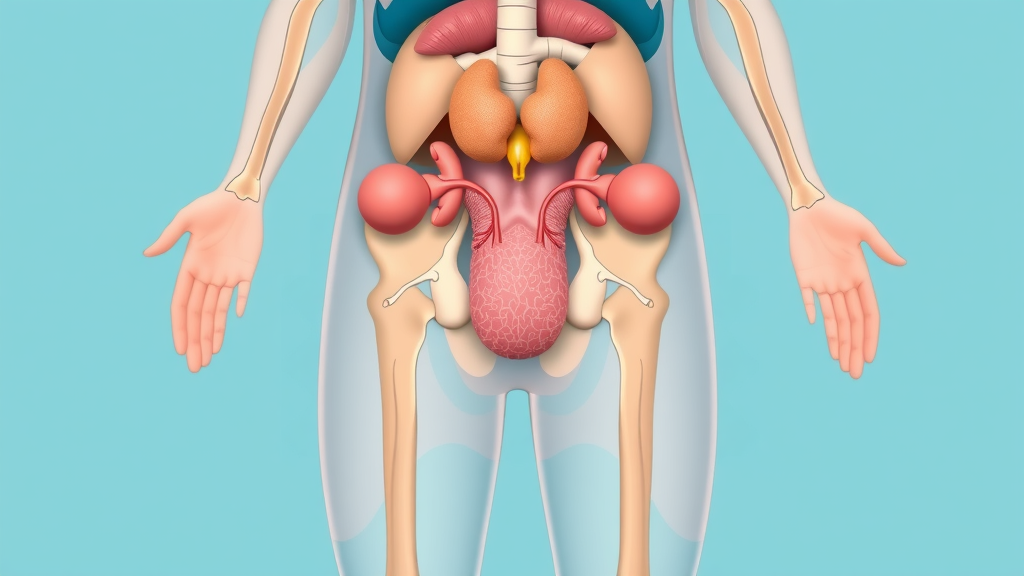
Primary Hypogonadism and the Role of the Testes
Primary hypogonadism occurs when the testes themselves can’t produce adequate testosterone. This may result from genetic conditions, such as Klinefelter syndrome, testicular injury, or even treatment for cancer. In these cases, the problem lies at the hormone’s source. Low testosterone levels in the blood, in combination with symptoms, strongly suggest an issue with testicular function.
Men with primary hypogonadism may also experience problems with sperm production , leading to fertility issues in addition to testosterone deficiency symptoms. Addressing the root cause requires specialist input and sometimes lifelong hormone support.
Secondary Hypogonadism: Pituitary Gland and Brain Regulation
Secondary hypogonadism refers to situations where the brain or pituitary gland —not the testes—fail to signal for sufficient testosterone production. This can result from tumors, pituitary disorders, or chronic health problems like obesity or diabetes. Sometimes, overuse of steroids or chronic illnesses can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance in the brain.
Because secondary hypogonadism may be reversible, identifying the source of the disruption—such as a treatable pituitary tumor or medication effect—can make a real difference in long-term outcomes and guide more targeted therapy.
Male Hypogonadism: Forms, Diagnosis, and Effects on Testosterone Levels
Male hypogonadism is the medical term for significantly low testosterone levels caused by failure of either the testes (primary) or pituitary gland /hypothalamus (secondary) to function properly. This condition is distinguished from normal or age-related declines by its underlying cause and severity. Doctors rely on a combination of testosterone level testing, examination, and sometimes genetic or imaging studies to identify the specific form.
The effects of male hypogonadism go beyond symptoms of low testosterone and include issues such as delayed puberty, infertility, and changes in bone and muscle development. Treatment depends on identifying the form—primary or secondary—and tailoring management accordingly.
Clinical Approach to Diagnosing Male Hypogonadism
Diagnosis starts with identifying classic signs and symptoms : persistent fatigue, poor sex drive , muscle and bone loss, or erectile dysfunction . Confirmatory blood tests are drawn multiple times to account for natural hormone fluctuations. Further tests check pituitary and brain health, including MRI imaging in certain cases.
The clinical process may be thorough but is necessary to rule out other issues and prevent missing deeper causes, such as treatable pituitary conditions. If male hypogonadism is confirmed, your doctor will suggest a customized care plan that may include replacement therapy or lifestyle strategies.
Life Stages Affected by Hypogonadism: Boys, Adults, and Seniors
Male hypogonadism can impact males throughout the lifespan. In younger boys, it disrupts puberty and physical growth. In adults, symptoms are often mistaken for stress or aging but may cause decreased muscle mass , motivation, and sex drive . Seniors may endure severe symptoms—especially increased risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular problems—unless underlying low testosterone is properly managed.
Early detection enables the best outcomes at every age. That’s why routine screening and talking openly about signs and symptoms are so valuable for long-term health and quality of life.
Low Testosterone Levels and Their Impact on Sex Drive, Muscle Mass, and Emotional Health
Beyond the obvious physical effects, low testosterone has far-reaching influence on mood, muscle mass , and sexual well-being. Testosterone deficiency is a leading contributor to loss of libido in men, erectile dysfunction , and decreased energy. The impact isn't limited to the body; the mind is often affected with increased risk of anxiety and depression.
Understanding these connections can empower men to seek timely care, supporting improvements in both physical and emotional well-being.
How Low Testosterone Can Cause Erectile Dysfunction and Reduced Muscle Mass
Low testosterone levels contribute to trouble achieving or maintaining erections—not solely because of reduced sex drive, but also through effects on blood flow, nerve function, and muscle strength. Testosterone helps preserve healthy muscle mass and bone structure; its deficiency leads to noticeable weakening, increased body fat, and loss of stamina.
Without adequate testosterone, your body struggles to repair and maintain tissue. This means even with exercise, building muscle can be frustratingly slow, and recovery is hampered. Addressing low testosterone can restore not only sexual function but also athletic capacity and everyday strength.
The Emotional Toll: Mood Changes, Motivation, and Mental Health
Fatigue and irritability are hallmark symptoms of low testosterone , but men may also experience changes in motivation, chronic sadness, or increased anxiety. The link between mood disorders and testosterone deficiency is well established; many men with low testosterone report loss of interest in hobbies, relationships, and overall life enjoyment.
These changes are not all in your head— testosterone is vital for brain chemistry and emotional stability . Failure to address hormonal imbalances allows symptoms to compound, leading to potentially avoidable declines in mental health.

Replacement Therapy for Low Testosterone: Evaluating Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Alternatives
For men with confirmed low testosterone and persistent symptoms, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a central treatment option. The goal of therapy is to restore levels to a healthy range, alleviating symptoms and improving both physical and mental function. Approaches vary, including gels, patches, injections, or implants, with choices tailored for effectiveness, convenience, and side effect profile.
However, not every man with low testosterone needs medication. Many will benefit from lifestyle modifications alone, and therapy should always be considered within the broader health context and with individualized goals.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Types, and How It Works
Testosterone replacement therapy is most effective for men with symptoms of testosterone deficiency and confirmed low levels. Benefits include increased muscle mass , improved sex drive , greater energy, sharper mental focus, and better overall mood. Common forms include topical gels, transdermal patches, intramuscular injections, and slow-release pellets, each with its unique pros and cons.
Individual preferences, costs, and lifestyle considerations all weigh into choosing the right therapy. Working with a hormone specialist or qualified urologist ensures therapy is optimized, side effects are monitored, and results are tracked over time.

Potential Side Effects and Safety of Testosterone Replacement
Like all medications, testosterone replacement therapy can have side effects . While side effects are usually mild and temporary, possible risks include acne, increased red blood cell counts, sleep apnea, or changes in cholesterol. Rarely, men may experience breast tenderness or local skin reactions with patches or gels.
There is also ongoing debate about TRT and its effect on the risk of prostate cancer ; current evidence suggests appropriate monitoring makes therapy safe for most. Discuss your personal and family medical history with your doctor before starting treatment.
"Testosterone replacement isn't for everyone. Discuss risks, benefits, and follow-up care with your specialist." — Urology Expert
Alternatives to Replacement Therapy: Lifestyle, Diet, and Exercise
For many, lifestyle shifts are the first defense against testosterone deficiency . Regular physical activity, especially strength training, can naturally boost testosterone production. Maintaining a healthy weight, sleeping 7–8 hours a night, managing stress, and limiting alcohol are all proven ways to support hormone health. Dietary changes—especially increasing healthy fats, lean protein, and micronutrients like zinc and vitamin D—make a meaningful difference as well.
If your testosterone level is borderline low or you have mild symptoms, these adjustments may reverse the problem without medications. Even if you need replacement therapy, lifestyle interventions remain a cornerstone of long-term testosterone health .
Addressing Low Testosterone Naturally: Evidence-Based Tips to Boost Testosterone Levels
If you're looking to manage low testosterone without medication, a few science-backed strategies can make a significant impact. Embrace a balanced routine that supports your body’s natural production and sustains energy, muscle strength, and mental clarity.
- Engage in regular exercise, especially strength training and interval workouts
- Keep your weight in a healthy range
- Aim for 7–8 hours of restful sleep per night
- Limit alcohol and avoid excessive drinking
- Prioritize stress management (meditation, deep breathing, hobbies)
- Maintain a balanced, nutritious diet (rich in lean proteins, healthy fats, and micronutrients)

Evidence-Based Solutions for Managing and Treating Low Testosterone
Who Is at Risk? Risk Factors and the Importance of Early Detection for Low Testosterone Level
Some individuals have a heightened risk for developing low testosterone . Knowing your personal risk factors can help you stay proactive and catch low levels early. Common risk factors include older age, obesity, type 2 diabetes, chronic diseases (such as kidney or liver disease), use of certain medications, history of trauma or radiation to the testes, and genetic syndromes.
- Age
- Obesity
- Chronic disease
- Medications
- Trauma
- Genetic syndromes
Why Early Diagnosis and Monitoring Matter for Long-Term Health
Early detection of testosterone deficiency means symptoms can be addressed before they seriously undermine your overall health. Monitoring testosterone also helps prevent complications such as osteoporosis, muscle loss, or mental health struggles. Men with risk factors should be especially aware of subtle changes and consider regular health checkups for timely diagnosis.
If you're over 40, living with chronic illness, or using hormone-affecting medications, talk to your doctor about periodic testosterone level screening as part of your routine wellness plan.
Addressing Misconceptions: Separating Facts From Myths About Low Testosterone Levels
There are plenty of myths about low testosterone , and clearing them up can empower better choices. For example, many believe only older men get low testosterone, or that treatment is always risky and symptoms are always obvious. In truth, men of all ages—including those in peak fitness—may experience testosterone deficiency.
- Low testosterone only affects older men— fact: It can impact younger individuals as well
- Testosterone therapy is dangerous for all— fact: With proper monitoring, risks are low
- Symptoms are always obvious— fact: Many symptoms are subtle and build over time
- Low levels don’t matter if you feel fine— fact: Even without symptoms, health may be at risk
Debunking Common Myths About Low Testosterone
Frequently Asked Questions on Low Testosterone and Male Hypogonadism
- How do you fix low testosterone levels?
- How do you increase your testosterone levels?
- What happens if a man has low testosterone?
- How to tell if testosterone is very low?
How do you fix low testosterone levels?
The solution depends on the cause but generally starts with lifestyle changes—exercise, weight loss, healthy sleep, and reduced stress. When clinical testosterone deficiency is confirmed, physicians may recommend medications or testosterone replacement therapy . Individualized treatment plans maximize safety and effectiveness for each man’s situation.
"Treatment should be individualized. Options include lifestyle changes, medications, and, if needed, testosterone replacement therapy under specialist care."
How do you increase your testosterone levels?
Boost your testosterone levels naturally by exercising regularly, focusing on sleep, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy diet. Avoid excessive alcohol and keep body fat in a healthy range. For some, medical interventions are necessary if lifestyle upgrades don’t restore normal levels.
"Boosting testosterone naturally involves sleep, exercise, and a healthy diet. Medical interventions are reserved for those with clinically low testosterone."
What happens if a man has low testosterone?
Without treatment, men with low testosterone may face persistent fatigue, reduced muscle mass , low sex drive , mood swings, higher risk for osteoporosis, and decreased quality of life. Long-term, low levels may also increase the likelihood of developing chronic medical conditions.
"Untreated low testosterone can lead to poor quality of life, increased risk for osteoporosis, and other chronic conditions."
How to tell if testosterone is very low?
Hallmark signs of very low testosterone include persistent unexplained fatigue, decreased libido, loss of muscle mass , erectile difficulties, and mood changes. These symptoms should prompt a blood test for confirmation, as diagnosis is based on both clinical presentation and hormone measurement.
"Hallmark signs include persistent fatigue, decreased libido, loss of muscle mass, and mood changes—always confirm with a blood test."
How to Recognize and Seek Help for Low Testosterone
Summary and Next Steps for Managing Low Testosterone
- Check for symptoms of low testosterone regularly.
- Get your testosterone levels tested if you experience persistent symptoms.
- Consult a healthcare provider for guidance on treatment options.
- Engage in lifestyle habits that support healthy testosterone production.
- Discuss replacement therapy options and potential side effects with your physician.
Take Control of Your Testosterone Health: When and How to Get Help
"Awareness is the first step toward effective management. If you suspect low testosterone, seek expert advice and take proactive action today."
What You'll Gain From Addressing Low Testosterone
- Better mood and energy
- Improved muscle mass and strength
- Restored libido and sexual health
- Greater overall wellbeing
Take the first step—identify your symptoms, get tested, and collaborate with your doctor to improve your testosterone health and overall quality of life.
If you’re interested in understanding the bigger picture behind declining testosterone levels, it’s worth exploring why men today have, on average, only half the testosterone of previous generations. This deeper dive into environmental, lifestyle, and societal factors can help you make more informed decisions about your health and prevention strategies. For a comprehensive look at the root causes and actionable insights, visit why men today have half the testosterone: key insights . Expanding your knowledge in this area can empower you to take proactive steps for long-term vitality and well-being.
 Add Element
Add Element  Add Row
Add Row 




Write A Comment